June 7, 2022
Nala Ogaada welcomes the completion of the federal presidential election on April 15, 2022 and the election of the House of The People (HoP) on April 24, 2022. While the formal conduct of the presidential election proceeded without incident, the parliamentary election period was marred by a power struggle at the highest office in the Federal Government of Somalia (FGS) adding complications and delays in an already overdue and lengthy election. Formal election talks began in 2019 but the recent process was only initiated after Prime Minister Roble was handed the task of completing the election in May 2021.
Nala Ogaada, a consortium composed of seven non-partisan national election observer, deployed 70 (35 women) observers throughout Somalia during the 2021/22 electoral process. Between July 2021 and May 2022, Nala Ogaada collected 1,503 observation reports from all six federal member states and Banadir Regional Administration (BRA). Observers conducted months of pre-and post- election observation of the Upper House elections, assessed HoP election preparations, visited polling stations, attended public events, and conducted meetings with electoral stakeholders including traditional leaders, candidates, representatives of women, youth and marginalized communities, security forces and other civil society organizations and activists.
Nada Ogaada observers also posted 1,469 incidences on Somalia’s election on Ushahidi, an online platform which means “testimony” in Swahili. The crowdsourcing platform allowed users to submit incident reports through mobile phones or the Internet. See https://somaliaelections.ushahidi.io/views/map for more information on the types of electoral information Nala Ogaada collected using Ushahidi.
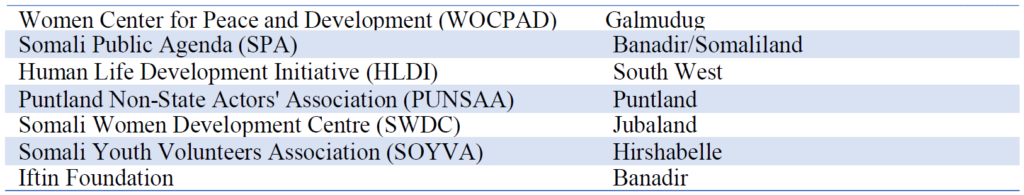
Ogaada’s observers came from seven organizations that followed international election observation standards to observe the electoral process. These seven organizations, and the states in which they observerd, were:
Key Findings
The 2021/22 electoral process was guided by ad hoc political arrangements based on a “4.5 power sharing formula” in which four major clans receive an equal portion of the seats in parliament with a collection of minority clans receiving a half-share of seats. Election procedures were guided by a political agreement rather than the established legal framework for elections. Election management was conducted by interim bodies with no role for the constitutionally-established NIEC. Electoral dispute resolution was likewise managed by an ad hoc body, the EDRC, rather than existing justice institutions. The process essentially repeated the arrangements used in 2016.
Election management was based on limited written guidance on election procedures and with a notable absence of any established framework for sub-clan seat allocation which limited candidate and voting delegate eligibility. The election calendar was subject to multiple and extensive delays that required political intervention to get back on track.
Each member of parliament was elected by 101 voting delegates, selected by a five-person committee of the sub-clan assigned the seat. While the adopted polling procedures were generally implemented properly, half of all MPs were elected non-competitively by a show of hands when opposing candidates withdrew. Many races completed by secret ballot had heavily lop-sided results.
The process failed to implement the agreed quota of 30% women representation in parliament and reached only 20%, a decline from the 24 % women elected in 2016.
Election Administration
The parliamentary elections were administered by a temporary appointed body – the Federal Election Implementation Team (FEIT) – comprised of 21 members. FEIT was joined by 11- member State Election Implementation Teams (SEIT) in each Federal Member State (FMS) which managed polling stations in two locations per state.
FEIT members fell short in several areas including alleged partisan engagement with election administration. For example, the FEIT chairman, Mohamed Hassan Iro an ally of then Somali federal president Mohamed Abdullahi Mohamed (“Farmaajo”) and six other members were removed in December 2021 following accusations of violating the neutrality of the election. PM Roble also dismissed six members of the 2020/2021 EDRC. The decree alleged the sacked members of the committee (including chairperson Hussein Mohamed Mohamud) abused their entrusted roles for objectives contrary to those expected from them and contravened the electoral Code of Conduct. Further, the decree accused the six members of mingling in politics, which is off-limits to them.
During the course of the HOP election, it became apparent that FIET, SEITs and the federal government worked almost as separate entities rather than collaborating.
Upper House Elections
Upper House (UH) elections were initially announced for July 25, 2021, with HoP elections to follow between August 10 and September 10, 2021. Delays started almost since the announcement. Jubaland held the first UH election and elected four (of its eight) UH seats on July 29, followed
by South West (five of eight seats) on August 2. The UH elections were completed on November 13 when Galmadug completed the UH elections for its final two seats.
South West was the only FMS with all of its seats contested. In three FMSs, the majority of seats were uncontested: all seats (100 percent) in Galmadug; nine of 11 (82 percent) in Puntland; and six of 11 (55 percent) in Somaliland. Even for the seats where polling was conducted, the margin of victory in 20 out of 24 seats was greater than 2:1, meaning only four seats (two in Hirshabelle and two in Somaliland) were settled by competitive margins.
At the end, nearly 50 percent of the successful candidates won their seats uncontested, elections were not held during the announced timeframe, and only 14 of 54 (26 percent) seats went to women, short of the required 30 percent.
House of the People Electoral Framework
A September 17, 2020 political agreement proposed an election model largely similar to that of the 2016-2017 process with minor modifications: a 275-member House of the People (HoP) with polling conducted in two locations per FMS; the number of voting delegates per parliamentary seat would rise from 51 to 101, and an expanded committee would review and approve individuals to serve as voting delegates. The 30 percent women’s quota would be maintained.
Instead of one-person, one-vote elections, fewer than 28,000 Somalis would be casting a ballot in the HoP elections.
House of the People Election
The conduct of the HoP elections and the announcement of final results were subject to continued delays.
The HoP election began formally with the election of four seats from Somaliland on November 1, 2021. With fewer than 50 seats elected by the end of 2021, the National Consultative Council (NCC) issued a January 9, 2022 communique that set a new deadline of February 25, 2022 to conclude the HoP elections. Only two constituencies – Banadir and Somaliland – met the extended deadline. The deadline was again pushed to March 15 with Galmudug and SWS completing their seats, followed by Puntland on March 18. Hirshabelle and Jubaland struggled to complete their elections. Hirshabelle was the last state to conduct a poll for the HoP election on May 6, 2022 with two remaining seats, one of which (HoP#135) belonged to MP Amina Mohamed who was killed in a March 2022 suicide bombing attack in Beledweyne.
Seats were allocated across FMS in accordance with the 4.5 power sharing formula in which the four major clans of Somalia receive an equal share of seats (61) and marginalized clans receive a half share (31).
Observers reported that candidates were largely able to exercise freedom of mobility (in the context of security and Covid precautions) and their freedom of association and expression at community meetings. Observers were generally able to attend meetings and other events at which aspirants announced their candidacy and called on traditional elders, clan and community members, women, youth and other gathered, for their support. This experience provides a good foundation for expanding the right of Somalis to participate in public and political affairs.
Polling was managed by SEIT officials. Observers found overall general compliance with the written procedures and most polls functioned without interruption or formal complaints.
The right to vote was severely restricted. The decision of Somalia’s political leaders against one- person, one-vote elections led them to rely once again on the appointment of several thousand delegates to select office-holders. Each HoP seat was elected by 101 delegates, though in the case of Somaliland, some delegates elected more than one seat. Delegates were selected by a five- person delegate selection committee and received training on the polling process.
The combination of seat allocation by sub-clan and a limited number of voters resulted in a lack of fair competition as 50% of all HoP seats elected had opposing candidates stepping down, leaving one candidate to be “elected” by a show of hands. In the seats elected by secret ballot, most were elected by extremely wide margins. These patterns and results raise serious questions about the integrity and credibility of the process as representative of the electoral hopes of the Somali people.
Presidential Election
The parliamentary committee for the presidential election certified the highest ever number of presidential candidates at 39 with each candidate paying a $40,000 registration fee. Prior to the election, three candidates withdrew, leaving 36 contenders including the incumbent federal president, two former federal presidents, a former prime minister, a former deputy prime minister and a sole female presidential candidate, Fowziya Haji Aden.
The African Union Transition Mission in Somalia (ATMIS) managed election security for the 329 parliamentarians; (54 UH, 275 HoP) gathered in Afisyoni Hanger, Mogadishu Airport, to elect the president on April 15, 2022.
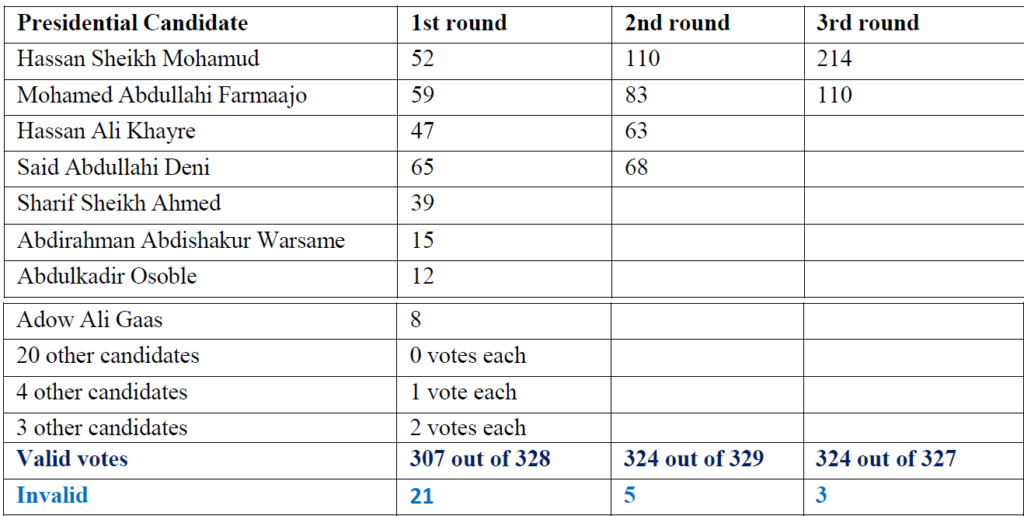
In the presidential election, if no candidate wins two-third majority (220 votes) in the first round, the four candidates with the most votes advance to a second round. If no candidate wins two-thirds majority in the second round, the top two finishers proceed to a third round with the winner elected by simple majority.
Said Deni, the State President of Puntland, won in the first round of election results. He was followed by former president Hassan Sheikh Mohamud, incumbent president Farmaajo and former PM Hassan Khayre. Former president Sharif Sheikh Ahmed did not pass. In the second round, no candidate won two-thirds, leaving the top two candidates – Hassan Sheikh Mohamud and Farmaajo
– proceeded to a third and final round. Hassan Sheikh Mohamud received elected 214 votes to Farmaajo’s 110, thus reaching the two-thirds mark and becoming Federal President of Somalia.
The table below shows the results of each round of the presidential election:
Electoral Disputes
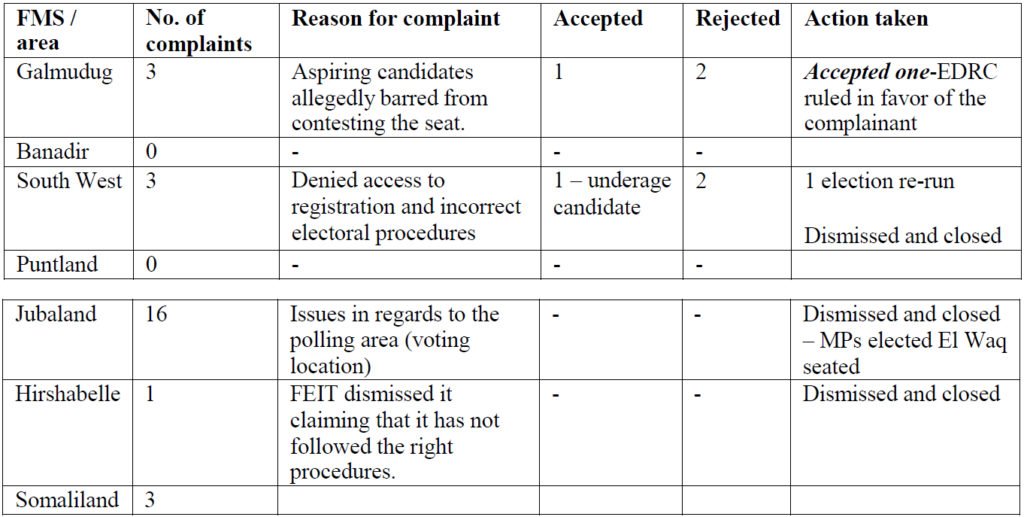
The Election Dispute Resolution Committee (EDRC) was established under the 17 September 2020 political agreement. The EDRC was tasked to resolve formally submitted complaints from candidates for both the UH and the HoP elections.
During the HoP election an estimated 26 seats were formally disputed, three from South West, one from Hirshabelle, three from Somaliland, three from Galmudug and 16 from Jubaland. Except for the three seats from South West, 16 from Jubaland, and one from Hirshabele, the remaining disputed six seats remain un-resolved. Some candidates that laid claim to seats decried the lack of transparency in the electoral process, while others claimed they were not allowed to sign up as formal candidates (e.g. HoP#203 and HoP#217). These cases did not move forward or were formally resolved presumably for the sake of completing the elections in a timely manner.
However, being one of the most substantial disputes, the 16 seats in Jubaland become a focal point of contention in the final days of the HoP election. Elections were conducted in two locations (El Waq and Garbaharey) generating two competing sets of 16 MPs each. While Garbaharey was the officially designated polling location for the seats, security concerns and a strained relationship between the Kismayo administration and the Garbaharey administration led to an impasse. The newly elected leadership of the HoP certified the 16 MPs elected in El Waq, putting an end to the controversial and disputatious Jubaland elections.
Another disputed seat lingered in Hirshabelle where Fahad Yasin initially won HOP # 86 but the FEIT removed him from the certified list of elected MPs, rejecting Fahad’s claim to the seat on the grounds that his election was not in line with the electoral procedure. Fahad appealed to the Supreme Court which rejected his case, stating that it has no jurisdiction over the election of the seat based on the constitution. During the course of the HoP election, it became apparent that FEIT, SEITs, Federal Member States (FMS) and FGS worked almost as separate entities rather than collaborating to mediate issues and disputes.
The table below summarizes the formal complaints to EDRC:
Election Finance
Election financing was not transparent with little public reporting on the election budget and no clear policy in place regulating election funds. FGS contributed a portion of the overall election budget and supplemented the rest through funding from the international community.
The NCC also recommended the establishment of the Electoral Financial Management Board consisting of the Electoral Committee at the FGS level, FMS, and the Office of the Prime Minister. In accordance with the electoral budget, an election finance committee would set the FMSs election expenditure quota in compliance with Somalia’s financial management regulations. Reports suggest the finance committee acted as the central financial management body for all financial matters of the election period.
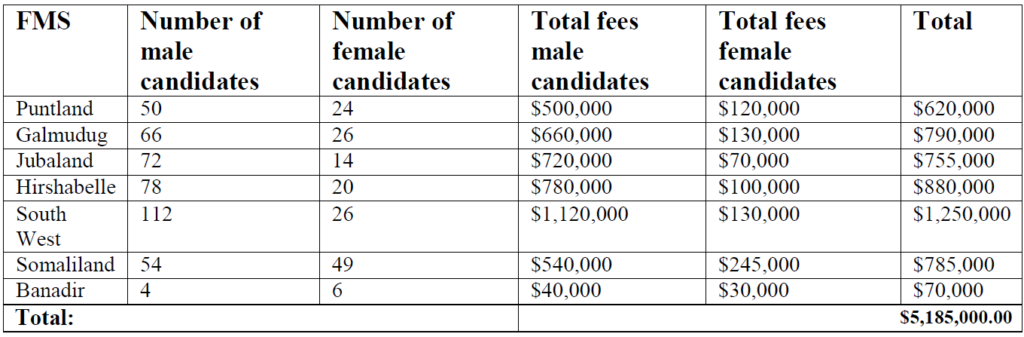
As per the political agreement signed by the NCC, the registration fee for male candidates was
$10,000, for female candidates $5,000. Based upon an unofficial tally of the total number of candidates for the 275 HoP seats, an estimated $5,185,000 million would have been generated by candidate fees. This was intended to be channeled into election process funds for each FMS. Reports vary as to how these funds were distributed with some states opting to set up a fund through their own SEIT to have direct access to the funds for their elections.
All elements of election finance were difficult to verify owing to a lack of transparency in election budget management and an absence of public reporting.
The following is the breakdown of the male and female candidates in each state and the estimated amount collected by the electoral body:
Women’s Participation
The women’s quota benchmark of 30% of elected seats was set by an agreement of the NCC that each clan with three seats must allocate a slot for a woman. Although advocated for thoroughly by women Goodwill Ambassadors, women candidates, youth advocates, academics, women’s rights activists and political experts, the 30% women quota was not achieved by any FMS. Somaliland led with 28% seats won by women followed by Galmudug (24%), Southwest (18%), Jubaland (16%), Puntland (14%), and Hirshabelle (10%). The 11th Parliament of Somalia now has 66 female parliamentarians or 20% of the combined Upper House and HoP seats, marking a decrease from the 24% elected overall in 2016.
Somalia’s female population of approximately 7.97 million, nearly equals their male counterparts but the participation and role of women in politics and decision-making is extremely limited, sustaining and continuing gender-based roles and inequalities.
Prior to the election, there were concerns that the level of representation of women would decrease. This, unfortunately, came to pass as female candidates struggled to access financial support to hold campaigns and lacked the political networks and connections of their male counterparts. Men have long dominated leadership and political roles, largely due to deeply ingrained traditional prejudices and preconceptions leading to minimal networks for women to use in elections. It is now clear that the clan-based political environment is not conducive to women and the repercussions of the lack of representation will most likely continue to be unfavorable for women in the coming five years unless male parliamentarians rally to support both universal suffrage and special measures to promote women’s political participation. Overcoming this obstacle, will play a greater role in Somalia’s journey to a potential democratic election, where fair and just are paramount
On a positive note, MP Sacdiya Samatar was elected as Deputy Speaker in the HoP. Sacdiya is the first woman to be elected to this position.
Marginalized Group Participation
Minority clans’ participation was reported throughout the pre-election period. Local and international organizations promoted and advocated for minority participation in the electoral process. Observers reported that minority clans’ participation in the pre-election period was unrestricted and the broader environment was conducive to their involvement in electoral activities and events.
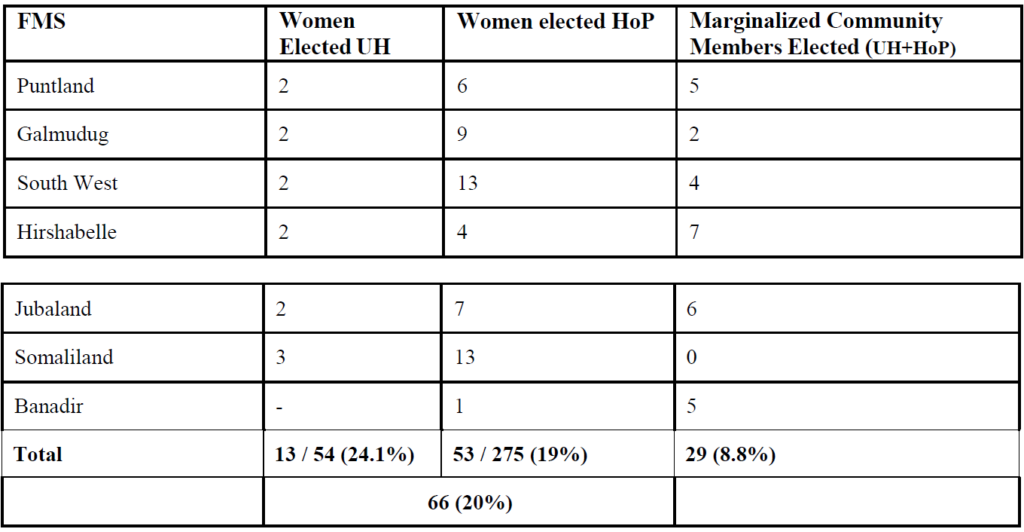
This table below show the number of women and marginalized clan members elected to the combined membership of the Upper House and HoP:
Election Security
Some elements of election security showed marked improvements compared to previous elections with fewer overall casualties and deaths directly linked to the election. Almost all formal polling location activities have taken place amid calm and peaceful environments but Nala Ogaada observers documented that electoral delegates, observers, and media workers faced multiple security challenges including COVID restrictions on public gatherings (thereby limiting observable election campaign activity), limited mobility owing to security measures, the ongoing threat of violence, and specific community tensions incidents where some candidates and traditional leaders objected to the SEIT allocation of seats.
Observers and media also faced instances of police abuse (e.g. failure to recognize observers and media official accreditation) and had difficulty accessing polling locations in incidents of partial and/or late issue of FEIT permission letters to security, exposing observers at security checkpoint delays. In Mogadishu, security forces barred observers from access to the Afiyonsi Hangar to observe the election of the HoP Speaker on 27 April.
In a notable violent incident in Beledweyne, the second polling location of Hirshabelle, a large number of people, including incumbent MP Amina Mohamed Abdi, were killed by a suicide bomber mission by Al-Shabab. In addition, Puntland’s second polling location of Bosaso was the site of heavy fighting and suicide bomb attacks which were partially linked to the electoral elections of the 16 seats in Bosaso.
Recommendations
Nalaa Ogaada’s observation mission gathered a total of 1,503 reports nationwide. The key characteristic of the 2021/22 election process is the concentration of power and political will amongst a select group of individuals and political actors. The vast number of Somalis are not linked to the selection of their candidates, which was left at the discretion of clan elders. It is unlikely that a handful of people can accurately represent the needs of entire sub-sets of communities and clans. The election of 2021/2022 was expected to deliver on the promise of one person, one vote elections. That did not come to pass and instead, political leaders reverted to the
- system of power-sharing among clans. The myriad election issues point to one conclusion: That the 4.5 system is not representative of the needs of the Somali people and that many are denied having a voice in the leaders that will drastically affect their lives. Now is the time for Somalia to learn from this election period and move forward as a nation where every voice
Based on this, Nala Ogaada makes the following recommendations:
- Both the constitution and the legal framework for elections should protect women’s direct engagement in public decision-making and assure their equal Special measures should be introduced to ensure women compose a minimum of 30% of elected seats (e.g. a legal framework to guarantee implementation of the 30% quota).
- We recommend the Auditor General of FGS audit the single treasury account to track the election finance and to publicize the amounts collected from all contributing parties as well as all election-related expenditures.
- We encourage political leaders to accept and encourage competition based on initiative, ideas and political agendas, in order to promote democracy, development and confidence of people with their leaders/representatives.
- Future elections should be conducted on the basis of one-person, one vote and administered by NIEC according to a legal framework for elections. However, NIEC could take note of some lessons from the 2021/22 experience, including:
- Ensure it retains independence free of political or partisan interference;
- Avoid unjustifiable internal conflicts among commissioners enabling them to maintain the confidence of election stakeholders;
- Work closely with political parties and candidates to share information and manage electoral disputes in an impartial process;
- Adhere to an established electoral calendar with clear guidance on the time allowed for each step of the electoral process;
- Adopt and implement all rules and electoral procedures in accordance with the legal framework;
- Promote and ensure aspirant candidates do not face unfair obstacles in their effort to stand for elected office;
- Ensure all election officials and other election participants have adequate training and equipment to conduct polling effectively and impartially;
- In collaboration with civil society organizations, conduct civic education on all parts of the election process, and;
Ensure a fair accreditation process for independent domestic observers with appropriate access to all elements of the electoral process.
Nala Ogaada is a non-state, non-partisan joint effort of Somali citizen observers from seven organizations, supported by Creative Associates International’s Bringing Unity, Integrity, and Legitimacy to Democracy (BUILD) Somalia project, with funding from the United States Agency for International Development (USAID). Nala Ogaada is comprised of Somali Women Development Centre (SWDC), Human Life Development Initiative (HLDI), Somali Public Agenda (SPA), Somali Youth Volunteers Association (SOYVA), Women Center for Peace and Development (WOCPAD), and Puntland Non- Actors Association (PUNSAA), and IFTIN Foundation.
Joint Statement of Somalia National Elections 9 June 2022




![]()

 Loading...
Loading...


























